There are three core components (see Figure1): i) The soil-plant model for a digital representation of the soil-plant system; ii) Physics-aware machine learning algorithms to approximate the soil-plant model; and iii) Data assimilation framework to digest Earth Observation data to update the states of soil-plant system. To address these digitalization challenges, the conceptual workflow for a soil-plant digital twin engine is presented in Figure 2, which consists of three pillars: “forward modelling”, “physics-aware machine learning”, and “Earth Observations”.
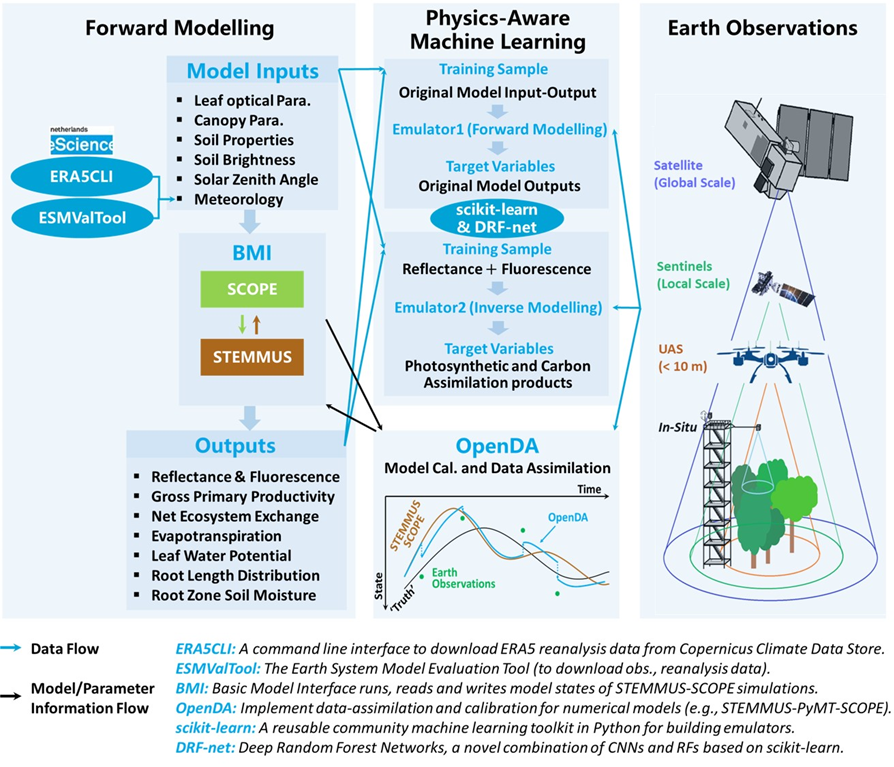
Figure 2 Conceptual workflow of the soil-plant digital twin engine.

